test for interosseous membrane tear|Syndesmotic ankle injury (high ankle sprain) : solution interosseous membrane injury 6. MRI. MRI has been shown to accurately detect injuries to the ligamentous structures of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis 1-3. The anterior . 800.257.8787. Email us. Financial Professionals Individual Investors. Under the leadership of TIAA, we invest in the growth of businesses, real estate, infrastructure, farmland and forests while building long-term relationships with clients from all over the globe.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Tottenham Hotspur. Veja as estatísticas de Tottenham Hotspur em 2023-24 na ESPN (BR). Inclui artilheiros, líderes de assistências e cartões.
High Ankle Sprain & Syndesmosis Injuries are traumatic injuries that affect the distal tibiofibular ligaments and most commonly occur due to sudden external rotation of the ankle. Diagnosis is suspected clinically with . Diagnosis can be difficult. Clinicians should consider the possibility of syndesmotic injury in athletes with pain or injury around the ankle or lower leg. Treatment too is different .
The Syndesmosis Squeeze Test of the ankle is a common orthopedic test to assess for syndesmosis injuries at the ankle after inversion trauma. interosseous membrane injury 6. MRI. MRI has been shown to accurately detect injuries to the ligamentous structures of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis 1-3. The anterior .1. Dorsiflexion External Rotation Stress Test (Kleiger's Test) Determines rotator damage to the deltoid ligament or the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Performed by having the knee flexed by 90 degrees with the ankle in neutral position and . The MRI is a better diagnostic tool for looking at soft tissue injuries including ligament and interosseous membrane tears. Who gets a high ankle sprain? The incidence of .
Tests for a syndesmosis injury external rotation stress test, squeeze test and interosseous membrane tenderness length should be performed if the mechanism suggests a syndesmosis .
To do the provocative tests to diagnose an occult injury or syndesmotic injury of the ankle, do the gravity test or do the abduction/external rotation stress views or do weight .The provocative tests used to evaluate an acute syndesmotic injury include the squeeze, external rotation stress, Cotton, fibular translation, and the cross-leg tests. The squeeze test is performed with the patient sitting on the edge of .
(10b) Just anterior to image 10a, a small amount of joint fluid protrudes superiorly into the normal interosseous synovial recess (arrow). The interosseous ligament is the lower margin of the interosseous membrane, and is visible as .
Purpose In the last two decades, a strong interest on the interosseous membrane (IOM) has developed. Methods The authors present a review of the new concepts regarding the understanding of forearm physiology and pathology, with current trends in the surgical management of these rare and debilitating injuries. Results Anatomical and biomechanical .
Background: Injuries of the interosseous membrane (IOM) of the forearm are frequently unrecognized, difficult to treat, and can result in a devastating sequelae for the wrist and elbow. Purpose: The purpose of this review article is to evaluate the dignosis, biomechanics, clinical results, and propose a treatment approach to this rare complex entity.TESTS. POSITION OF THE ANKLE. STRUCTURES INVOLVED. . Interosseous Membrane. Knee is flexed 90 0 and gastrocnemius is relaxed. Move the calcaneus and talus to each side as a unit. . If this causes pain then must consider a tear of the anterior tibiofibular ligament. Depending on severity the interosseous membrane may be involved. Pain will .
The distal tibia and fibula are held tightly together by the syndesmosis membrane, and the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments. A syndesmotic sprain or high ankle sprain is an injury to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis with possible disruption of the distal tibiofibular ligaments and interosseous membrane. Create Group Test Enter Test Code . all acute traumatic TFCC tears. operative. arthroscopic vs. open debridement and/or repair . indications. . Radial head fracture with an interosseous membrane injury extending to DRUJ . unstable relationship between ulna .
Provocation tests: Watson's test "scaphoid shift test" Test is performed by the examiner stabilizing the scaphoid with one hand while using the other hand to move the wrist from ulnar to radial deviation. Positive test: The examiner should feel a significant "clunk" and the pt will experience pain. Decreased range of motion due to pain To examine the anatomy and function of the forearm interosseous membrane by exploring the anatomical insertions of the central band (CB) on the radius and the ulna and by quantifying the length of the intact ligament and replacement grafts located at the original CB attachment sites and alternative locations.
Physical examination combined with MRI to determine the damage to the interosseous membrane is significant in guiding the treatment of ankle syndesmosis injury with interosseous membrane injury. In the past, inserting syndesmosis screws was the gold standard for treating ankle syndesmosis injury. However, there were increasingly more .Injury to the interosseous membrane of the forearm typically occurs in conjunction with disruption of the radial head and the distal radioulnar joint. Frequently, the true extent of injury is not initially appreciated, and patients may develop longitudinal instability of the forearm, with wrist pain, forearm discomfort, and instability. .Conversely, three cases of er C type fractures had IOM tears that remained distal to the level of the fibular fracture. Conclusions . The level of the fibular fracture does not correlate reliably with the integrity or extent of the interosseous membrane tears identified on MRI in operative ankle fractures. One cannot consistently estimate .
The anterior interosseous nerve arises off the median nerve in the proximal forearm, approximately 5-8cm distal to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.A 2018 cadaver study (n=50) summarized that the anterior interosseous nerve branched from the median nerve anywhere from 1.5 to 7.5 cm (mean = 5.2 cm) distal to the intercondylar line.. It is comprised of the C5-T1 .
Often interosseous membrane tears are associated with adverse impacts on forearm rotation. MRI-assisted diagnosis has been used for mid-substance tears of the interosseous membrane but is expensive and not widely available. . In surgery, you will do the radius pull test. More than 3mm of translation is concerning for longitudinal forearm . tear in the interosseous membrane between the shafts of the tibia and fibula. As this tear progresses up the interosseous membrane, all the forces are placed more proximally along . stress test under fluoroscopy (8). Type of screw fixation for repairing the syndesmosis:
The injuries can be divided and categorized according to the direction of instability, whether they are reducible, and the presence of arthrosis (Table 48.1).Pseudo-instability, caused by radial head excision or fracture without IOM injury, can be confused with a longitudinal instability because the radius moves proximally by 2–7 mm even with an intact CC (Fig. 48.2).During preparation of the specimens, when only half the interosseous membrane had been divided, performance of the test was not found to produce any noticeable increase in the size of the tear. Discussion These results suggest that the radius joystick test may be used for the intra-operative diagnosis of interosseous membrane disruption and .
Reconstruction of the central band of the interosseous membrane is an emerging procedure implemented in the treatment of longitudinal radioulnar dissociation (LRUD), usually in its chronic setting, after Essex-Lopresti injuries of the forearm. . due to an overlooked partial tear of the IOM . The ‘radius pull test’ is considered positive .Large sustained loads occur after radial head resection with concurrent interosseous membrane tears, resulting in the proximal migration of the radius and disruption of the distal radioulnar joint. Ultimately, the treatment option for severe membrane disruption combined with proximal migration of the radius is the creation of a single bone forearm.Objectives: To correlate interosseous membrane (IOM) tears of the ankle to the height of fibular fractures in operative ankle fractures. Design: Prospective clinical trial. Setting: University Level 1 trauma center. Patients: All patients admitted with a closed operative ankle fracture were included. Of 93 patients originally evaluated, 73 patients had adequate MRI for evaluation.
The Interosseous membrane is a strong fibrous sheet of connective tissue that acts as a long ligamentous membrane between two bones, also known as a syndesmosis joint. These membranes travel from proximal (high) to distal (lower) in an oblique direction and create a natural anatomical divider between the compartments of the forearm and lower leg. The anterior interosseous nerve (AIN) is the terminal motor branch of the median nerve. It branches from the median nerve in the proximal forearm between the two heads of the pronator teres muscle to run deep along the interosseous membrane. From proximal to distal, it innervates the flexor pollicus longus (FPL), the index and long fingers of the flexor digitorum . The surgical pathology in 3 forearm fractures/dislocations (2 Galeazzi injuries and 1 Essex-Lopresti injury) shows a longitudinal oblique tear of the interosseous membrane, parallel to its major .
The crural interosseous membrane (IM) extends between the interosseous crests of the tibia and fibula, helps stabilize the tibio-fibular relationship and separates anterior compartment muscles from posterior compartment muscles of the leg.Previous microscopic and anatomical studies of the crural IM have shown the angulation of fibers,1,2 diameter of IM fiber .Injury to the interosseous membrane of the forearm typically occurs in conjunction with disruption of the radial head and the distal radioulnar joint. Frequently, the true extent of injury is not initially appreciated, and patients may develop longitudinal instability of the forearm, with wrist pain, forearm discomfort, and instability. This article outlines various treatment strategies, . The interosseous membrane of the leg is also referred to as the middle tibiofibular ligament. This ligament extends through the fibula and tibia’s interosseous crests and separates the muscles .a through forearm rotation and actively transfers forces from the radius to the ulna. The interosseous membrane’s unique functional capabilities result from its anatomic and histologic organization, which produces a stiff structure with elastic properties capable of maintaining large loads. The interosseous membrane’s load transferring ability reduces the forces placed on .
The interosseous membrane (IOM) is stretched between the two bones of the forearm. . in this case, combined with a fracture-impaction of the radial head and a tear of the triangular fibrocartilaginous complex (TFCC) of the wrist resulting in Essex-Lopresti syndrome (Fig. 10.1) [1]. . If the IOM is broken, one manages to generate a real .
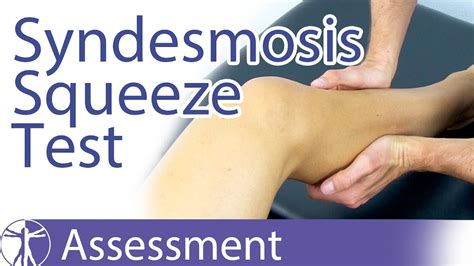
The Syndesmosis Squeeze Test
Syndesmotic ankle injury (high ankle sprain)
WEB26 de nov. de 2021 · Home team. Score/Time. Away team. sexta 26/11/2021. FT. Cruzeiro. 0 - 0. Náutico. sexta 26/11/2021.
test for interosseous membrane tear|Syndesmotic ankle injury (high ankle sprain)